How it works | Manuka Honey | Antibacterial Activity | Treatment
Honey is well known for its antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory properties and has for years some types have been used as a healing agent for wounds, burns and ulcers. Difficult and severe wounds have been known to react to honey and heal effectively. Therefore, honey dressings in wound care are popular and have found their way into modern medicine especially where conventional treatment of antibiotics and antiseptics are proving ineffective. More and more, medical honey is now being used in the treatment of different types of wounds including surgical incision sites, traumatic wounds, minor burns or first and second degree burns, leg ulcers, diabetic foot ulcers, sloughy wounds and pressure ulcers.
For years now, many studies have been conducted and much research been done into the nature of honey and its characteristics. Controlled trials were conducted and critical reviews presented. Although studies continue, there are published reports about the healing properties of honey and its effective use in modern medicine.
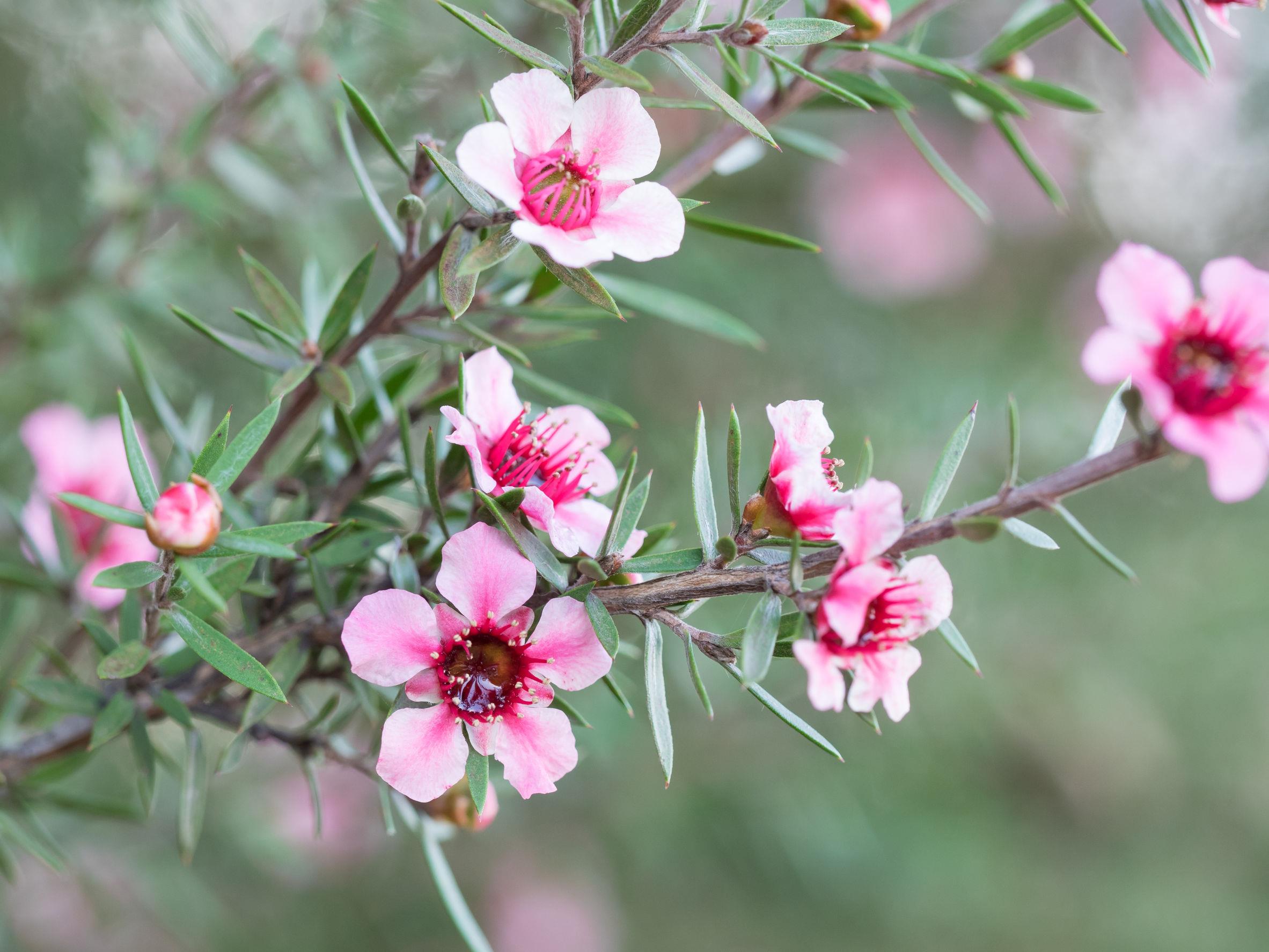 Different types of honey work differently. All honey may not have the same healing effect and the higher the antibacterial activity of the honey, the stronger the healing power.
Different types of honey work differently. All honey may not have the same healing effect and the higher the antibacterial activity of the honey, the stronger the healing power.
Honey from the manuka tree, which is native to New Zealand, is said to have exceptionally high antibacterial activity because of its additional non-peroxide antibacterial component. This means the presence of high degree of antibacterial phytochemical activity. Manuka honey has been found to have an effective impact on difficult-to-heal wounds and burns. It keeps the wound bed clean of necrotic tissue and can also work in the presence of wound fluid, blood, and tissue.
Many kinds of honey produce hydrogen peroxide on dilution but in the case of manuka honey (Leptospermum scoparium), hydrogen peroxide has not been noticed. Undiluted honey has a broad spectrum antibacterial activity due to its high sugar content and lower water content but when it is diluted, this activity is lost. But in the case of manuka honey, this does not hold true. The presence of a heat stable antibacterial component, methylglyoxal, maintains the antibacterial activity even when it comes in contact with the wound fluid and becomes diluted. This non-peroxide activity is important because factors such as acidity, catalase and protein-digesting enzymes in wound fluids all work towards reducing the hydrogen peroxide antibacterial effectiveness. So, honey needs to have non-peroxide activity in order to create a healing environment.
The therapeutic properties of honey depend on its bioactive components. In manuka honey, a bioactive component called methylglyoxal is said to contribute to the antibacterial activity. Honey, particularly Manuka honey, has been seen to have an antibacterial effect against fungi including Staphylococcus aureus and Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
Sterilized, laboratory-tested honey should be used in the treatment of infected wounds. Honey dressings are available in various forms – gel or ointment, honey-impregnated tulle, get sheets and honey-impregnated calcium alginate.
 |
 |
 |
||
| Medihoney Gel Dressing | Medihoney Sheet Dressing | Medihoney Rope Dressing |
Medihoney dressings are quite popular for management of wounds and burns. They contain active manuka honey providing a moist, occlusive environment which is conducive to optimal wound healing. The wound exudates get absorbed allowing the alginate to form a gel and the dressing to be easily removed. These types of dressings can be used on chronic or acute wounds and can form an important component of wound bed preparation.
Disclaimer: All content found on our website, including images, videos, infographics and text were created solely for informational purposes. Our content should never be used for the purpose of diagnosis or treatment of any medical conditions. Content shared on our websites is not meant to be used as a substitute for advice from a certified medical professional. Reliance on the information provided on our website as a basis for patient treatment is solely at your own risk. We urge all our customers to always consult a physician or a certified medical professional before trying or using a new medical product.